Metal 3D printing is transforming various industries. It offers unique advantages for creating complex geometries and lightweight structures. However, selecting the right Metal 3D Printing Materials is crucial for success. Each material has distinct properties, impacts performance, and cost.
Different applications require different materials. Stainless steel, titanium, and cobalt-chrome are popular choices. They each provide unique characteristics that can influence the final product's integrity. Yet, not every material suits every task. Missteps can lead to costly failures. Understanding these materials can feel overwhelming, but it's essential.
Designers must weigh pros and cons carefully. Cost, strength, and durability are vital concerns. Experimentation may yield unforeseen challenges. Material choices are not always clear-cut. Embracing the intricacies of Metal 3D Printing Materials unveils a path to innovation.
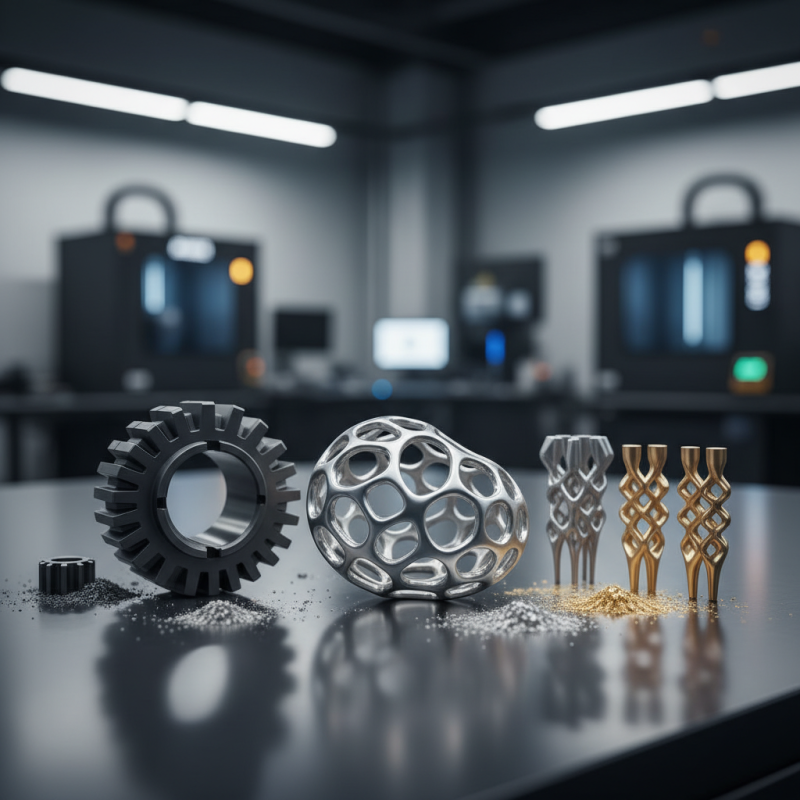

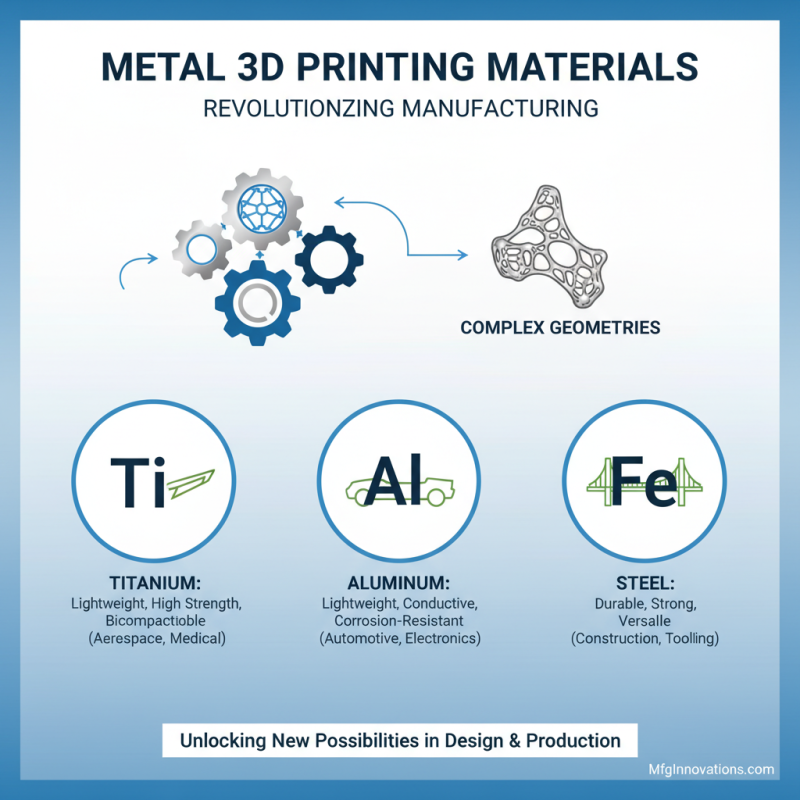
Metal 3D printing materials are revolutionizing manufacturing. They enable the production of complex geometries that traditional methods can't achieve. Common materials include titanium, aluminum, and steel. Each offers unique properties for specific applications.
Titanium is favored for its strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It's extensively used in aerospace and biomedical fields. Aluminum, on the other hand, is lightweight and offers excellent thermal conductivity. For heavy-duty applications, steel is often selected for its toughness. These materials can be expensive, and the printing process can be slow.
Understanding the properties of each material is essential for successful outcomes. The selection often depends on the intended use. While some materials may provide superior strength, they could also pose challenges in processing. This requires careful consideration of factors such as cost and performance.
When discussing commonly used metals in 3D printing, a few materials stand out. Stainless steel is a favorite among many manufacturers. Its robustness and corrosion resistance make it ideal for functional parts and prototypes. According to a report by Wohlers Associates, stainless steel accounts for approximately 48% of metal 3D printing materials used in the industry. This underlines its popularity and reliability.
Another key material is titanium. Known for its lightweight and strength, titanium is favored in aerospace and medical applications. However, the high cost and complicated printing process of titanium can be barriers. Recent studies suggest that titanium powder costs can reach up to $400 per kilogram. This raises questions about the scalability of projects using titanium, especially for small businesses.
Aluminum is another metal increasingly being used in 3D printing. Its lightweight nature makes it attractive for various applications. Yet, challenges exist in achieving the right mechanical properties. Some users report inconsistent quality in aluminum prints, leading to potential failures. This inconsistency prompts a need for better material control and testing practices in the industry.
When it comes to 3D printing, selecting the right metal alloy is crucial. Metals like titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum are popular choices. Each alloy has unique properties that cater to different applications. Titanium offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It's ideal for aerospace components. Stainless steel is versatile, providing good corrosion resistance. It’s often used in medical devices. Aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective. It’s suitable for automotive parts.
Tips: Don't rush your selection. Consider the specific demands of your project. Evaluate mechanical properties, temperature resistance, and corrosion levels. Always prototype first. This step can save you time and costs later.
However, not all materials perform equally. Some alloys may be difficult to print with. They might warp or require extensive post-processing. These factors can complicate the design process. It's essential to conduct thorough research on the chosen material. Experimentation is key; be ready to adjust your approach as needed. Regular feedback from your printing process is vital for success.
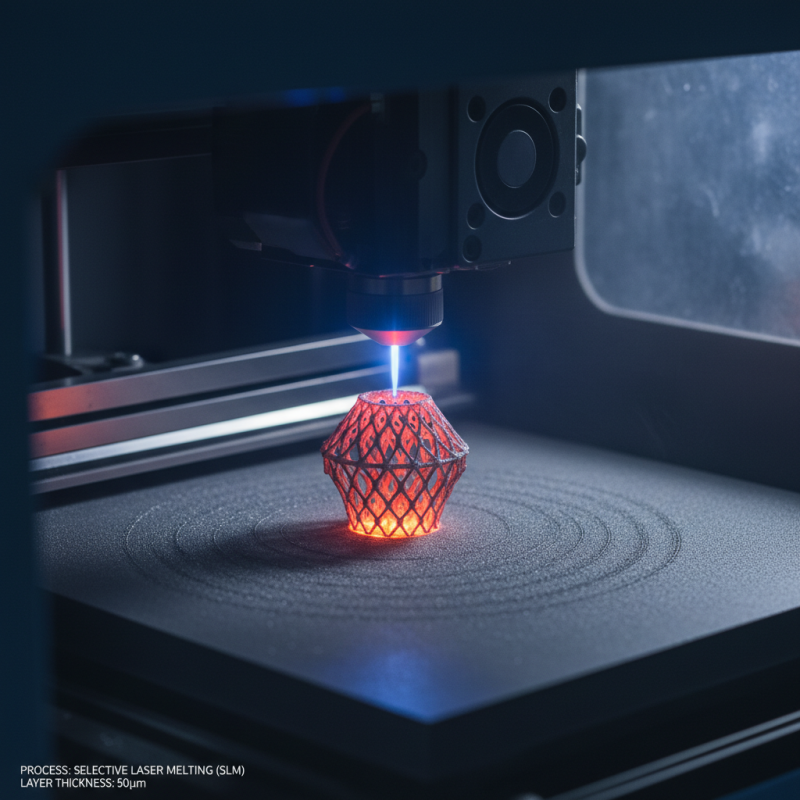
Advanced metal 3D printing techniques are transforming how industries approach manufacturing. One prominent method is Selective Laser Melting (SLM). This process uses a laser to melt and fuse metal powders layer by layer. It allows for complex geometries that traditional methods can't achieve. However, achieving optimal parameters can be challenging. The right combination of speed and power is crucial. Slight adjustments may alter the final part's strength.
Another key technique is Electron Beam Melting (EBM). EBM operates in a vacuum, making it suitable for reactive materials. This technique also provides impressive build speeds, but it often requires extensive post-processing. Parts may not come out as pristine as expected. One must consider the possibility of residual stresses. These stresses can lead to warping, necessitating careful design and planning.
Metal Binder Jetting offers a different approach. It uses a binding agent to adhere metal powder, which is subsequently sintered. While less expensive and faster than SLM, the surface finish may not meet high standards. Users often find the need to improve finishing processes. Each method has unique advantages and drawbacks. Recognizing these nuances is essential for optimal results in advanced metal 3D printing.
The landscape of metal 3D printing is rapidly evolving. Recent studies show a projected increase in market growth, with the industry expected to reach $4 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the importance of innovative materials in enhancing printing capabilities and product performance.
Key trends include the development of high-performance alloys. These materials enable complex geometries that traditional manufacturing techniques can't achieve. For instance, titanium and aluminum alloys are gaining traction due to their lightweight properties and strength. The aerospace sector particularly values these attributes, leading to a 25% rise in demand for titanium powder in 2023.
However, challenges remain. The cost of metal powders can be prohibitive, affecting adoption rates. Additionally, issues such as porosity and surface finish still need addressing. Companies are actively researching solutions to improve these aspects. The focus on sustainable materials is also on the rise, with recycled powders becoming an area of interest. This shift reflects a growing awareness of environmental impact.
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Point (°C) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 7.9 | 1400 | 600 | Food Industry, Medical Devices |
| Titanium | 4.5 | 1660 | 900 | Aerospace, Medical Implants |
| Aluminum | 2.7 | 660 | 300 | Automotive, Consumer Goods |
| Nickel Alloy | 8.5 | 1455 | 950 | Aerospace, Marine Engineering |
| Copper | 8.96 | 1085 | 210 | Electrical, Thermal Applications |