Magnesite Refractory Bricks are essential materials in high-temperature applications. Their unique properties make them ideal for various industries. These bricks are primarily composed of magnesium carbonate and are known for their excellent stability and resistance to thermal shock.
In steel manufacturing, Magnesite Refractory Bricks play a crucial role in furnaces and kilns. They ensure the integrity of structures under extreme conditions. These bricks can withstand high heat without degrading, which is vital for efficiency. However, their production process can be resource-intensive and may raise concerns about environmental impact.
Understanding the applications of Magnesite Refractory Bricks can lead to improved practices. Industries must reflect on the sustainability of using these materials. As technology advances, better options are emerging, but traditional uses persist. Exploring these insights helps identify future challenges and opportunities in the field.
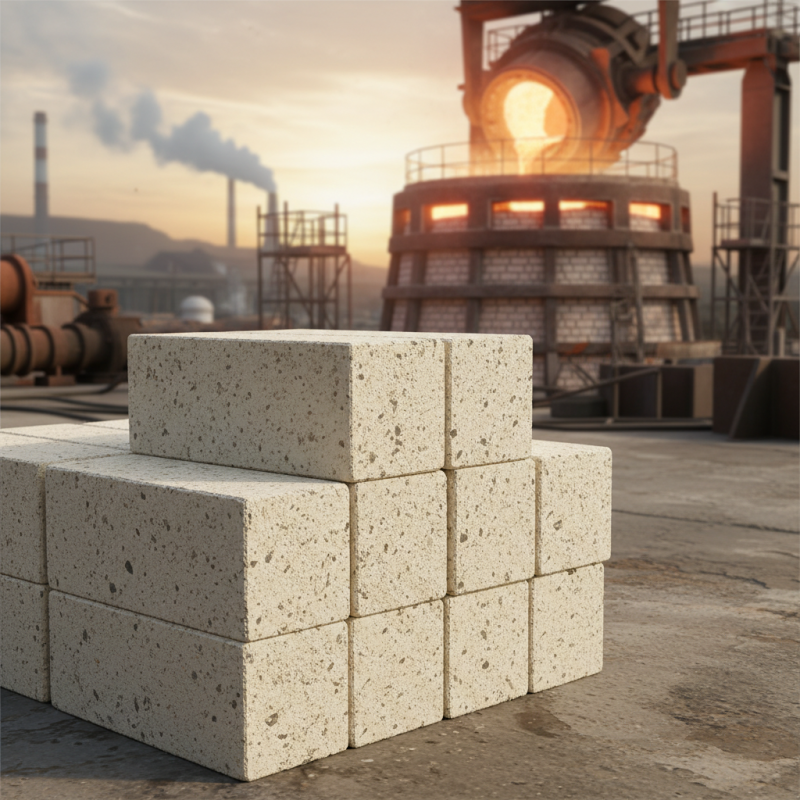

Magnesite refractory bricks are essential in high-temperature applications. Their primary composition is magnesium oxide, derived from natural magnesite. This unique structure grants them superior thermal stability. They can withstand extreme heat, making them ideal for use in furnaces and kilns. These bricks also resist basic slags, which enhances their durability in smelting processes.
The properties of magnesite refractory bricks are quite notable. Their thermal conductivity is relatively low, which helps maintain heat within furnaces, contributing to energy efficiency. They also have good mechanical strength, but this can vary based on the manufacturing process. Some bricks may exhibit cracks under stress. This inconsistency can be a downside for certain applications.
In practical uses, the versatility of magnesite refractory bricks is both an asset and a challenge. They are utilized in steel production and glass manufacturing. However, not all grades perform equally in every application. It's essential to select the right type for specific needs. This selection requires careful consideration of operational requirements and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors helps in making informed choices about their use.
The manufacturing process for magnesite refractory bricks involves several critical steps. Initially, high-quality magnesite ore is mined. This raw material is then subjected to calcination at high temperatures. The calcination helps to remove impurities. After this, the calcined magnesite is ground into a fine powder.
Next, additives are mixed into the magnesite powder. These can include binders and other materials that enhance performance. The mixture is then shaped into bricks using various methods, such as pressing or casting. This shaping process is essential for ensuring the bricks have the desired density and strength.
After shaping, the bricks undergo a drying phase. It’s important to control the drying temperature carefully. If the moisture is not adequately removed, it can lead to defects. Finally, the bricks are sintered at extremely high temperatures. This process helps develop the final properties of the refractory brick. However, achieving the right conditions can be tricky. Small variations can significantly impact the overall quality and performance of the bricks.
Magnesite refractory bricks are crucial in industrial furnace applications. These bricks excel in high-temperature environments. They withstand extreme heat and thermal shock well. Therefore, they are often used in steel production, glass manufacturing, and cement kilns. Their ability to resist corrosion is vital for these industries.
In steelmaking, magnesite bricks line the electric arc furnace. They help maintain the furnace's temperature and protect it from slag erosion. In glassmaking, they provide excellent insulation. This property ensures consistent melting temperatures. However, improper handling can lead to cracks and reduced lifespan. This oversight can be costly for manufacturers.
Despite their advantages, magnesite bricks pose challenges. Their production requires careful quality control. Small impurities can weaken the structure. Additionally, suppliers often face transportation issues. The weight of these bricks can lead to logistical hassles. It's essential to address these concerns for optimal performance in industrial settings.
This chart illustrates the various applications of magnesite refractory bricks in industrial furnaces, highlighting their key areas of usage.
Magnesite refractory bricks are gaining attention in high-temperature industries. These bricks can withstand extreme heat, making them essential in steel, glass, and cement production. They are primarily composed of magnesium oxide, which has high melting points. According to industry reports, magnesite bricks can operate effectively at temperatures exceeding 1600°C.
Using magnesite refractory bricks offers several benefits. Firstly, they exhibit strong resistance to thermal shock. This feature minimizes the risk of cracking and ensures durability. Additionally, they possess excellent slag resistance, which is crucial in metallurgical applications. Studies show that implementing magnesite bricks can enhance operational efficiency by up to 20% in certain environments.
**Tips:** Ensure proper installation for optimal performance. Monitor the working environment regularly to identify any wear. Regular assessments can prevent unexpected failures and prolong the lifespan of your setup. Magnesite bricks also require attention during sourcing. Not all suppliers provide the same quality, leading to performance inconsistencies. Consider testing samples from different sources before large-scale procurement.
The magnesite refractory brick industry is experiencing significant shifts. Reports indicate a projected growth rate of over 5% from 2023 to 2030. Innovations in manufacturing processes are essential. Enhanced energy efficiency and sustainability are becoming critical driver trends.
The use of magnesite refractory bricks is expanding beyond traditional steel and cement industries. Emerging applications in the energy sector show promise. Companies are experimenting with new blends that improve performance and lifespan. Yet, challenges remain in standardizing these new materials. Without clear consensus, quality can vary widely.
Research highlights a key issue: the environmental impact of magnesite mining. The industry must balance demand with ecological responsibility. There are ongoing discussions on alternative materials that might reduce this burden. Striking this balance will be vital for future success in magnesite refractory technologies.






